How Urea Can Hydrate and Exfoliate Your Skin

Urea is a natural substance that your body makes and excretes in urine. It’s also a key ingredient in many skin care products, especially creams and lotions. Here’s what you need to know about urea and how it can benefit your skin.
Read More: Urea and Its Features and Applications
Contents
What Is Urea and How Does It Work for Skin Care?
Urea is one of the natural moisturizing factors (NMFs) that help keep your skin hydrated and smooth. NMFs are substances that attract and bind water molecules to the outermost layer of your skin, called the stratum corneum.
Synthetic urea is made in a lab and added to skin care products for its moisturizing and exfoliating properties. Urea works for skin care by:
- Moisturizing the skin cells by drawing water from the deeper layers of the skin and the air.
- Exfoliating the skin by breaking down the protein keratin that binds the dead skin cells together. This helps reduce flaking, scaling, and roughness of the skin.
- Enhancing the penetration and effectiveness of other medications, such as corticosteroids and antifungals.
What Are the Benefits of Urea for Different Skin Types and Conditions?
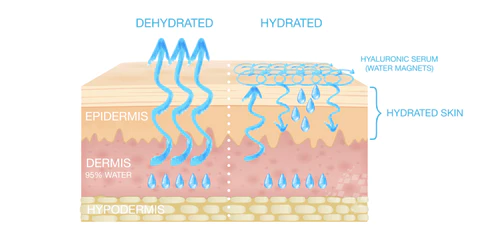
Urea can improve hydration, texture and appearance of various skin types and conditions. Some of the common uses of urea for skin care are:
Urea for Dry Skin
Dry skin is caused by a loss of NMFs in the stratum corneum, which leads to reduced water content and increased water loss through the skin. Urea can help restore moisture and prevent water loss by attracting and binding water molecules to the skin. Urea can also soften and smooth the dry, rough and scaly skin by removing the excess keratin.
Urea for Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema)
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that causes itching, redness, swelling and cracking of the skin. Urea can help relieve AD symptoms by moisturizing and soothing the irritated skin, reducing inflammation and itchiness, and enhancing the barrier function of the skin. Urea can also improve the absorption of topical corticosteroids, which are commonly used to treat AD.
Urea for Ichthyosis
Ichthyosis is a group of genetic disorders that cause dry, scaly and thickened skin that resembles fish scales. Urea can help treat ichthyosis by hydrating and softening the skin, reducing scaling and thickness, and improving elasticity and flexibility of the skin.
Urea for Fungal Nail Infections
Fungal nail infections are caused by fungi that invade the nail plate or nail bed, causing discoloration, thickening, brittleness and separation of the nail from the nail bed. Urea can help treat fungal nail infections by dissolving or peeling off the affected nail, allowing better penetration of antifungal medications into the nail bed .
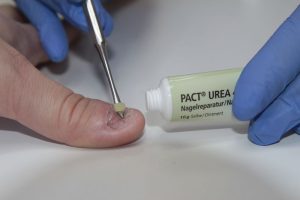
How to Use Urea Products Safely and Effectively?
Urea products come in different forms (creams, gels, lotions, shampoos) and concentrations (3-40%). The concentration of urea determines its function and potency. Higher concentrations have stronger exfoliating effects, while lower concentrations have more moisturizing effects. Here are some tips on how to use urea products safely and effectively:
Choosing the Right Concentration of Urea
The concentration of urea you need depends on your skin type and condition. Generally, creams with 10% urea concentration are suitable for hydrating normal to dry skin. Products with 20-30% urea concentration can help treat scaly skin conditions such as psoriasis, ichthyosis and eczema. Products with 40% urea concentration are used to dissolve or peel off dystrophic nails or thickened skin such as corns and calluses.
Applying Urea Products Correctly
Urea products should be applied to clean and dry skin, preferably after bathing or showering. You should follow the directions on the product label or consult your doctor or pharmacist for the appropriate amount and frequency of use. Urea products should be massaged gently into the skin until fully absorbed. You should avoid applying urea products to broken, irritated or infected skin, or to the eyes, mouth or mucous membranes.
Possible Side Effects and Precautions of Urea

Urea products are generally considered safe and well-tolerated, but they can cause some side effects or risks in some cases. Some of the possible side effects of urea products are:
- Skin irritation, burning, stinging, itching, or redness. These are more likely to occur with higher concentrations of urea or on sensitive skin. If these symptoms persist or worsen, stop using the product and seek medical advice.
- Allergic reactions, such as rash, hives, swelling, or difficulty breathing. This is rare but serious. If you experience any signs of an allergic reaction, stop using the product and get emergency medical help.
- Overdoses, such as nausea, vomiting, headache, confusion, or seizures. This can happen if you swallow urea products or apply too much of them on your skin. If you suspect an overdose, contact your local poison control center or get emergency medical help.
To prevent or minimize the side effects of urea products, you should:
- Do a patch test before using a new product. Apply a small amount of the product on a small area of your skin and wait for 24 hours to see if you have any reaction.
- Use the lowest effective concentration of urea for your skin condition. Start with a lower concentration and gradually increase it if needed.
- Use urea products only as directed. Do not use more than the recommended amount or frequency of use.
- Avoid contact with eyes, mouth or mucous membranes. If contact occurs, rinse thoroughly with water.
- Keep urea products out of reach of children and pets. Do not store them in high temperatures or near open flames.

Bottom Line
Urea is a versatile ingredient that can benefit various skin types and conditions by moisturizing, exfoliating and enhancing the skin. Urea products are available in different forms and concentrations to suit different needs and preferences. Urea products are generally safe and effective, but they can cause some side effects or risks in some cases. Therefore, it is important to use them correctly and cautiously.
If you have any questions or comments about urea in skin care, feel free to leave them below. Thank you for reading!
Read More: urea suppliers
sources:
Last Seen
















Users Comment
Sodium carbonate| Soda ash; features and applications
Copper Sulfate; Features and applications
Sulfur; Features and applications
Zinc sulfate; Features and applications
Urea; Features and applications
Sodium bicarbonate; Features and applications
Ammonium Sulfate; Features and applications
What is the use of caustic soda? An Overview of the caustic soda uses
Caustic soda flakes and the methods of production
Analysis of September manufacturing trends in Asia
The impact of growth in major Asian economies on petrochemical demand
Aramco loan $2 billion to Petro Rabigh to cover cash shortfall