What Is Bitumen and Why Is It One of the Most Strategic Industrial Materials?
Bitumen is a dense, black, highly viscous material produced by the vacuum distillation of crude oil. Composed of heavy hydrocarbons, asphaltenes, and resins, it is one of the most essential raw materials used in civil infrastructure, transportation, building construction, waterproofing systems, and the energy sector.
Its role is not limited to road asphalt; bitumen is also used in waterproofing membranes, industrial protective coatings, pipeline insulation, chemical industries, and the production of many industrial compounds.
The role of bitumen in infrastructure and road development
More than 90% of road construction and pavement projects depend directly on the performance of bitumen. Its quality determines:
- The durability of asphalt under heavy traffic
- The resistance of pavement to heat, cold, and climate variations
- The level of cracking, rutting, and fatigue in asphalt layers
- The service life and maintenance costs of roads and highways
Iran as a regional hub for bitumen production
With major refineries in Tehran, Bandar Abbas, Isfahan, Abadan, Shiraz, and Kermanshah, Iran is considered one of the key bitumen producers in the region. High production capacity allows both full domestic supply and significant export volumes.
However, professional buyers always look for suppliers that offer standard-compliant products, reliable analysis, and secure export packaging.
Through Shimico’s B2B marketplace, you can directly access profiles of verified bitumen suppliers, compare grades and prices, review analysis reports, and choose the best source for your project.
Top 10 Bitumen Suppliers in Iran
In Iran, bitumen is supplied by refinery plants, specialized packing companies, oxidized bitumen producers, emulsion plants, and official export houses. Below is an overview of ten key bitumen producers and suppliers that are active in both domestic and export markets.
| # | Supplier | Product Types | Packaging | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tehran Oil Refinery | Penetration Grades 60/70 and 80/100 | Drums, bulk | Tehran |
| 2 | Bandar Abbas Oil Refinery | Road and export-grade bitumen | Export drums, bulk | Bandar Abbas |
| 3 | Isfahan Oil Refinery | Grades 40/50 and 60/70 | Drums, bulk | Isfahan |
| 4 | Abadan Oil Refinery | Penetration and industrial grades | Drums, bulk | Abadan |
| 5 | Shiraz Oil Refinery | Construction and road bitumen | Drums | Shiraz |
| 6 | Kermanshah Oil Refinery | Grades 60/70, 85/25 | Drums, bulk | Kermanshah |
| 7 | Pasargad Oil Company | Penetration, oxidized, and emulsion bitumen | Export drums, bulk | Multiple plants across Iran |
| 8 | Jey Oil Company | 60/70, oxidized bitumen | Drums, jumbo bags | Isfahan, Bandar Abbas |
| 9 | Private export suppliers | Industrial and road grades | Export drums, bulk | Industrial hubs |
| 10 | Bitumen suppliers on Shimico | 60/70, 80/100, oxidized, emulsion, PG grades | Drums, bulk, jumbo bags | Nationwide / export |
Bitumen Buying Guide and Key Selection Criteria
Buying bitumen is a highly technical decision. An incorrect choice can negatively impact pavement performance, waterproofing efficiency, and the overall quality and service life of infrastructure.
Selecting the right grade, checking a reliable analysis, and understanding project conditions are three fundamental steps in professional bitumen procurement.
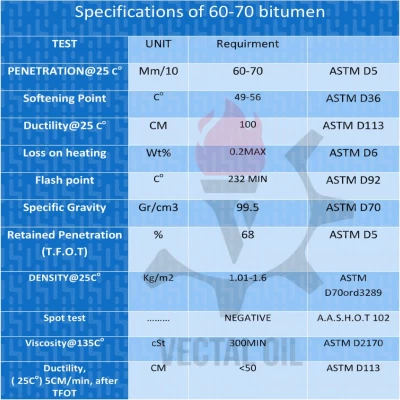
Step 1 – Reviewing the analysis report
Trusted suppliers provide a certified analysis sheet with each shipment. At minimum, you should carefully check:
- Penetration grade value
- Softening point
- Viscosity at different temperatures
- Solubility in CS2
- Specific gravity and weight loss
- Flash point
Each of these parameters determines how the bitumen will perform under actual field conditions and which type of project it is suitable for.
Step 2 – Choosing the right grade for your project
Bitumen grade must be chosen based on application type, climate, and construction method:
- 60/70: The most widely used grade for highways and heavy-traffic roads
- 80/100: Suitable for colder regions and areas with long winters
- 40/50: Ideal for hot climates with heavy traffic loads
- Oxidized bitumen: Used in waterproofing, membranes, cable insulation, and industrial sheets
- Emulsion bitumen: Used for prime coat, tack coat, cold asphalt, and rural road construction
- PG bitumen: Performance-grade bitumen designed for modern highways based on high- and low-temperature performance
Additional considerations for export buyers
If your target market is export, you should also consider:
- Type of packaging (new steel drums, palletizing, jumbo bags)
- Compliance with destination standards (ASTM, EN, ISIRI or client-specific specs)
- Drum quality (no rust, no leakage)
- Loading methods, storage conditions, and temperature control
- Customs regulations and export documentation
Types of Bitumen Produced in Iran and Worldwide
Bitumen is classified based on production method and performance behavior. Each category has specific characteristics and is selected for certain project types. The main groups are:
1. Penetration grade bitumen
The most common type used in road construction, including 40/50, 60/70, and 80/100. Classification is based on the depth of penetration of a standard needle at a specific temperature.
- 40/50 for very hot climates
- 60/70 as the standard grade for highways
- 80/100 for colder areas
2. Viscosity grade bitumen (VG)
VG10, VG20, VG30, and VG40 are categorized based on viscosity at different temperatures. These grades are more stable under temperature variations and are widely used in export markets.
3. Oxidized bitumen (blown bitumen)
Produced by blowing hot air through bitumen. This process:
- Increases hardness
- Improves thermal stability
- Makes the product more suitable for industrial waterproofing applications
Common grades include 115/15 and 105/35.
4. Bitumen emulsion
A mixture of bitumen, water, and emulsifier, designed for low-temperature applications and moist surfaces. Key advantages are lower fuel consumption, safer handling, and faster application.
5. Performance grade (PG) bitumen
The most advanced category of bitumen, engineered according to performance at both high and low temperatures. Typical grades include PG 58-22 and PG 64-16, widely used in modern highways and regions with severe temperature fluctuations.
Physical and Chemical Properties of Bitumen
Bitumen’s behavior in road construction, building applications, and waterproofing depends directly on its physical and chemical properties. Understanding these characteristics helps engineers and buyers select the right grade for each climate and loading condition.
Key properties of bitumen
- Specific gravity: typically between 1.00 and 1.05 g/cm³
- Flash point: usually above 230°C, providing safe handling at high temperatures if safety rules are followed
- Penetration: main criterion for penetration grade classification
- Softening point: indicates thermal resistance and stability at high temperatures
- Viscosity: determines flow behavior at different temperatures
- Solubility: insoluble in water but fully soluble in CS2 and toluene
- Thermal behavior: crucial for crack resistance and rutting performance
Why accurate analysis matters
Even small changes in penetration, softening point, or viscosity can significantly affect asphalt performance or waterproofing quality.
Harder grades perform better in hot climates, while softer grades are more suitable for cold regions. Therefore, a reliable analysis report is a mandatory requirement for every shipment, not just an optional document.
Bitumen Production Methods and Related Industrial Processes
Bitumen is produced through several main industrial processes, depending on the required grade and application. Each method changes the molecular structure and final behavior of the product.
1. Vacuum distillation (penetration bitumen)
In refineries, crude oil is distilled under vacuum, and the residue is penetration-grade bitumen (such as 60/70 and 80/100). This material is the base feedstock for many other bitumen products.
2. Air blowing (oxidized bitumen)
In this process, hot air is blown into heated bitumen under controlled conditions. The result is:
- Higher hardness
- Greater thermal and structural stability
- Improved performance in industrial waterproofing
Well-known grades include 115/15 and 105/35.
3. Bitumen emulsion production
Bitumen emulsion is produced by mixing bitumen, water, and emulsifier in special mixers. It is used where asphalt must be applied at lower temperatures or on slightly moist surfaces.
- Lower energy consumption
- Safer and more flexible application
- Higher speed of execution for light and rural projects
4. Cutback bitumen production
Cutback bitumen is obtained by blending bitumen with solvents such as naphtha or diesel to reduce viscosity and make it suitable for cold-applied asphalt or primer applications.
Industrial Applications of Bitumen
Bitumen is a fundamental material in numerous industries, providing protection, adhesion, durability, and waterproofing. The most important application sectors include:
Road construction and transportation
- All pavement layers (binder, wearing course, base)
- Urban and intercity roads
- Highways and expressways
- Heavy-traffic transportation corridors
Building and waterproofing applications
- Waterproofing membranes (bituminous membranes)
- Foundation sealing and tanking
- Roof insulation and damp-proofing
- Bituminous sheets and protective layers
Chemical and industrial uses
- Corrosion protection for pipelines
- Coating of oil and gas tanks
- Bituminous primers and adhesives
- Protective industrial and anti-rust coatings
Subsurface and heavy civil projects
- Dams and tunnels
- Subsurface structures and underground facilities
- Waterproofing of concrete structures
Packaging, Storage, and Transportation of Bitumen
Packaging and transportation play a critical role in preserving bitumen quality until the point of use. Proper packaging is especially important for exports and helps prevent leakage, contamination, and quality loss.
Packaging for penetration-grade bitumen
Penetration grades are usually supplied in two main packaging formats:
- Steel drums (150–180 kg): suitable for export and standard storage
- Bulk hot bitumen in tankers: ideal for large projects and continuous consumption
Packaging for oxidized bitumen
- 25 kg bags
- Blocks and solid moulds
- Export-grade jumbo bags
Packaging for bitumen emulsion
- Coated steel tanks
- IBC plastic tanks
- Coated drums
Standard storage conditions
- Dry, shaded warehouses away from direct sunlight
- Adequate ventilation to prevent vapour accumulation
- Preventing bitumen emulsion from freezing
- Proper palletizing and stacking of drums
Safe transportation of bitumen
For safe transportation of bitumen, the following principles should be observed:
- Using tankers designed for hot bitumen
- Controlling product temperature during the entire journey
- Preventing leakage or damage to drums in road or sea transport
Safety Guidelines for Working with Bitumen
Hot bitumen is a highly sensitive material. Skin contact or inhalation of dense fumes can cause serious harm. Strict adherence to safety practices during storage, transfer, and application is essential.
Essential safety measures
- Use heat-resistant gloves, protective clothing, and safety footwear
- Wear safety goggles when spraying or transferring hot bitumen
- Ensure proper ventilation in heating and storage areas
- Avoid overheating of storage tanks and boilers
- Inspect bitumen boilers and tankers regularly for leaks or structural issues
- Follow regulations for transporting flammable materials on roads
Following these guidelines helps protect workers’ health, reduce the risk of industrial accidents, and prevent costly project delays.
Bitumen Prices and Key Market Drivers
Bitumen prices are influenced by a combination of global and local factors, leading to specific volatility patterns in both domestic and export markets.
Understanding these factors helps professional buyers choose the right timing and structure for their purchase.
Main factors affecting bitumen prices
- Global crude oil price: the primary driver of bitumen pricing
- Bitumen grade: 60/70, 80/100, oxidized, emulsion, PG, etc.
- Quality and analysis level: higher quality often means higher price
- Type of packaging: bulk, drums, or jumbo bags
- Domestic logistics and loading costs: plant to port or border
- Exchange rate: direct impact on export prices
- Standards and storage costs: especially relevant for export operations
Why 60/70 and 80/100 grades are more volatile
These two grades have the highest demand in both domestic and export markets. As a result, even small changes in crude oil prices, packaging costs, or exchange rates can quickly affect their final selling price.
On Shimico, you can compare different bitumen grades such as 60/70, 80/100, oxidized, emulsion, and PG, review analysis reports and specifications, and contact verified suppliers directly to receive competitive offers and optimized delivery terms.